The integration of technology in dental practices is a key paradigm shift, not just a trend. Digitization in healthcare extends to dentistry, reshaping it with advancements such as digital imaging, laser treatments, artificial intelligence, and innovative dental implants. This revolution enhances dental procedure efficiency, improves patient experience by reducing pain and recovery time. However, it also presents ethical considerations requiring examination. Exploring, understanding, and addressing these implications are vital in this dentistry’s technological transition.
Understanding Dental Technology
Dental technology spans from innovative diagnostic tools to advanced treatment methods. Smart Toothbrushes are trending in this field, equipped with AI, sensors, and advanced software. They provide real-time feedback, monitor brushing habits, and deliver personalized advice for better oral health, marking a significant transformation in preventive dental care.
Wearable dental devices including smart braces and mouthguards utilize micro-sensors to monitor oral health and habits, detect issues early, and allow prompt intervention. They are effective in managing bruxism, malocclusion, and promoting patient compliance.
The Need for Technological Advancements
Advanced dental technology is essential for precision, efficiency, and patient comfort during procedures. This need is driven by increasing demands in the dental field. The benefits of digital advancements in dentistry are manifold, impacting both patients and practitioners positively.
Digital Advancements in Dentistry
Digital technology is integral to modern dentistry, enhancing precision, efficiency, and patient experience. Key advancements comprise:
- Smart Toothbrush Evolution: Embedded sensors and connectivity provide real-time feedback, improving user’s brushing techniques and oral hygiene. Data analysis identifies neglected areas or excessive pressure, preventing dental issues. User profiles enable customization to individual needs and preferences.
- Dentistry Augmented Reality: AR facilitates training, patient education, and surgical planning. It offers risk-free practice for dental students and helps patients visualize treatment plans, enhancing comfort and compliance.
These innovations are driving a shift towards proactive, personalized oral care in dentistry.
Benefits of Dental Technology
Dental technology’s benefits, including enhanced procedures and improved patient experiences, are numerous. Mobile Dentistry, through digital technology, offers remote dental care, improving accessibility for patients with geographical or physical constraints. This advanced practice extends dental care to underserved populations, optimizing patient convenience. Modern teeth whitening techniques, employing lasers and LED lights, deliver safe and effective results, reducing treatment time and possible side-effects. This increases patient satisfaction and efficiency in dental practices. Continued technological advancements are therefore essential in dentistry.
Digital Imaging in Dentistry
Digital technology’s advent has catalyzed a shift in dental practices towards digital imaging. This shift has amplified precision, efficiency, and affordability in dental diagnostics and treatment.
- Radiation Safety: Digital imaging amplifies safety by requiring less radiation than conventional radiography, fostering a safer environment for staff and patients.
- Lower Dosage: Digital systems necessitate up to 90% less radiation than traditional X-rays.
- Immediate Viewing: Instant image availability eliminates retakes and additional exposure.
- Imaging Affordability: Digital imaging has propelled cost-efficiency in the dental industry.
- Less Material: The absence of film and developing chemicals trims costs.
- Time-Efficiency: Instantaneous digital images decrease patient chair time, boosting practice efficiency.
Laser Technology for Treatments
Laser technology advances dental procedures by reducing discomfort, increasing treatment accuracy and efficiency. Applications include cavity detection and gum disease treatments, revolutionizing dental practices.
Benefits of Laser Dentistry
Laser technology revolutionizes dentistry, enhancing safety, precision, and patient comfort. Established laser safety protocols protect health. Lasers provide unparalleled accuracy, preserving healthy tissue and minimizing trauma. This precision speeds healing and reduces complications. Lasers coagulate blood vessels, reducing bleeding. Laser dentistry decreases pain perception, improving comfort and potentially eliminating anesthesia need. Consequently, patient satisfaction rises, possibly increasing regular dental visits.
Laser Technology Applications
Laser technology, in dentistry, has diverse, transformative applications, offering precision in cavity preparation, soft tissue surgeries, and tooth whitening, while minimizing tissue damage. Strict laser safety protocols are essential to avoid accidental exposure causing eye and skin injuries. However, laser technology has limitations, unsuitable for filling interdental cavities or large cavities needing crown preparation. Additionally, laser equipment costs surpass traditional dental tools. Yet, when used correctly and safely, laser technology can significantly advance dentistry.
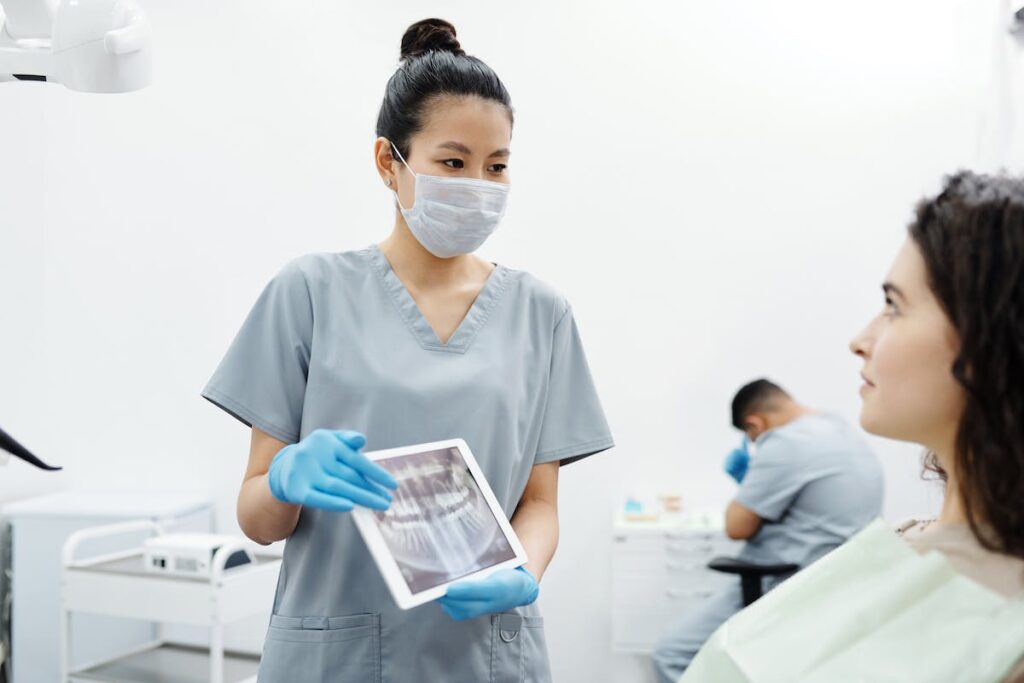

Role of AI in Dentistry
Artificial intelligence (AI) plays a transformative role in dentistry, enhancing accuracy and efficiency through AI-enhanced diagnostics and robotic surgeries.
AI diagnostics utilize algorithms to interpret dental radiographs, identifying potential pathologies that might escape human detection. Additionally, machine learning models predict future oral health complications from historical data, facilitating preventive care and personalized treatment plans.
Robotic-assisted surgeries in dentistry offer superior precision, minimizing human error risk. These robotic systems perform micro-movements beyond human capabilities, assuring optimal outcomes in intricate procedures.
AI’s integration in dentistry augments, not replaces, dentist skills. It supports informed decision making, improved patient results, and enhances practice efficiency. As AI technology evolves, its significance in dentistry will continue to amplify.
Benefits of 3D Printing
3D printing in dentistry cuts costs, streamlines treatment, minimizes waste, and elevates patient satisfaction. It enables in-house production of dental restorations, implants, and orthodontic appliances, eliminating expensive external lab services. This reduces overhead costs and speeds up treatment. Additionally, 3D printing’s precision minimizes material waste, aiding sustainable dentistry. It also ensures accurate dental appliance fit, enhancing patient comfort and treatment effectiveness. As 3D printing technology evolves, it promises to transform dental care delivery, making it more comprehensive, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly.
Intraoral Cameras Usage
Intraoral cameras, a dental technology innovation, enhance diagnostic precision by providing detailed oral cavity views. Key aspects of their usage include:
- Camera Maintenance: Regular inspection, lens cleaning, and software updates ensure optimal camera performance and accurate diagnosis.
- Patient Perception: Visual aids from high-resolution images improve patient understanding, engagement, and treatment compliance.
Details are as follows:
- Camera Maintenance: To maintain camera performance and diagnostic accuracy, regular inspection, lens cleaning, and software updates are essential. Regular inspection can identify and rectify physical damage, ensuring the camera’s lifespan.
- Patient Perception: Intraoral cameras provide high-resolution images, acting as visual aids that help patients understand their dental issues. This understanding promotes active patient participation in oral health care and better adherence to treatment plans.
Computer-Aided Design and Manufacturing
The transformative integration of CAD/CAM technology into dental practices offers precise restorations and workflow efficiency. However, successful CAD/CAM adoption in dentistry necessitates careful consideration of several factors. This succinctly captures the subject, predicate, and object, ensuring optimal processing by machine learning and semantic search engines.
Advantages of CAD/CAM Technology
CAD/CAM technology in dentistry yields precision, time efficiency, and enhanced patient satisfaction. It allows accurate 3D models for dental prostheses, minimizing errors from manual methods. Regular software updates and staff training can mitigate limitations. The technology expedites workflow, enabling faster treatment. Opting for fast-curing materials can cut down manufacturing time further. The precision and efficiency minimize treatment time and adjustments, hence improving patient comfort and satisfaction.
Implementing CAD/CAM in Dentistry
CAD/CAM technology’s implementation in dental practices is crucial given its advantages such as cost-effectiveness, productivity increase and precision. However, technology resistance, particularly from older dentists due to complexity fears, obsolescence, and significant initial investment, can hinder this process. Overcoming this requires comprehensive training and clear demonstration of long-term financial benefits. Despite challenges, CAD/CAM technology implementation is a strategic step towards efficient, accurate and patient-friendly practices, representing progress in dentistry’s digitization.
Impact of Tele-Dentistry
Tele-dentistry has digitally revolutionized dental care, impacting practitioners and patients. Its legislation has legitimized and catalyzed its adoption, though virtual consultation limitations exist.
Key impacts are:
- Regulatory: It extends dentists’ service reach, mandates compliance with tele-dentistry legislation including privacy laws, and requires update alignment with evolving telehealth regulations.
- Clinical: It enhances access for rural or underserved communities, improves efficiency via digital record keeping and scheduling, but faces limitations like inability for hands-on diagnosis.
- Patient Experience: It provides convenience through virtual consultations, promotes preventative care via regular virtual check-ups, but may induce apprehension due to lack of physical dentist interaction.
Virtual Reality Training for Dentists
Virtual Reality (VR) revolutionizes dental education by enabling immersive, interactive training. Though challenges like cost and technical complexities persist, the potential for skill enhancement through this innovative tool is significant.
Benefits of VR Training
VR training in dentistry offers numerous advantages. VR equipment maintenance is simple, contributing to its cost-effectiveness. VR’s immersive learning strategies enhance hands-on experience.
Key benefits of VR training are:
- Improved Learning: VR’s immersive, interactive environments result in superior understanding and retention.
- Risk-Free Learning: VR enables dentists to learn from mistakes without real-world repercussions.
- Cost Efficiency: VR training, with its simple equipment maintenance and less need for physical resources, is cost-effective.
Implementing VR in Education
Implementing VR in dental education enhances practical training and patient outcomes. Considerations for successful integration include cost, accessibility, and training. High-grade VR equipment is expensive, requiring cost-effective strategies for procurement and maintenance. Accessibility extends beyond device availability, requiring technical support and educator training. Fair access for all students, irrespective of socio-economic background, is crucial. Thus, comprehensive planning considering cost, accessibility, and training is key to successful VR integration in dental education.
Challenges in VR Adoption
VR adoption in dentistry faces hurdles related to cost, technical proficiency, and patient comfort.
- Cost: The financial burden of VR integration includes initial investment, maintenance, and upgrades of VR tools.
- Technical Knowledge: Operating VR demands specific technical skills, potentially requiring further training or hiring specialized personnel, escalating expenses.
- Patient Comfort: VR unfamiliarity may induce anxiety in patients, impacting their satisfaction, a vital element for successful dental practice.
Addressing these issues is essential for fully leveraging VR in dental practices.
Evolution of Dental Software
Dental software evolution, driven by affordability and data security, has transformed dental practices. Falling development costs made software adoption economically viable, enabling digitalization of smaller practices and fostering competition among providers. The rise of cyber threats amplified the importance of data security in dental software, leading to the implementation of encryption, secure cloud storage, and robust access controls. Therefore, dental software evolution is crucial in integrating technology into dental practices, providing affordable solutions that prioritize data security.
Innovations in Dental Implants
Dental implants are experiencing innovation in design, materials, and cost, driven by technology. Specifically, technology assists in creating durable, affordable implants tailored to individual needs.
Three main areas of dental implant technology advancement include:
Design: Software precision allows 3D mouth models for accurate, custom-fit implants. This leads to:
- Enhanced comfort and aesthetics
- Increased durability, reducing replacement necessity
Materials: Incorporation of new materials like zirconia offers a natural look and enhances durability.
Cost: Technological progress in manufacturing results in:
- Higher production efficiency
- Labor cost reduction
- Greater patient affordability
These advancements are transforming dental practices, improving patient outcomes and accessibility. Ongoing tech evolution promises further advancement.
Future Predictions for Dental Tech
The future of dental technology is projected to see a significant rise in tech-driven orthodontics and advancements in smart toothbrushes. Tech-driven orthodontics, integrating digital technology, will see growth, particularly through 3D imaging, printing, and artificial intelligence. These advancements allow for more precise and efficient creation of customized orthodontic appliances and enable predictive treatment outcomes and personalized patient care.
Simultaneously, smart toothbrushes with advanced features such as real-time feedback, pressure control sensors, and AI-driven brushing habit analysis offer a better, personalized oral care experience. The coupling of toothbrushes with smartphone apps encourages tracking and proactive management of oral hygiene habits.
These predictions, based on current trends, indicate that increasing technology adoption in dental practices will lead to more effective, efficient, and personalized care, marking a transformation in future oral healthcare.
Patient Experience With Modern Dentistry
Dentistry’s evolution, driven by technology, has revolutionized patient experience, enhancing comfort, precision, and personalization. Key areas include Dental Anxiety Reduction and Patient Data Security.
- Dental Anxiety Reduction: Technology’s role in less invasive procedures diminishes patient anxiety. For example, lasers enable painless treatments, and virtual reality fosters a calming environment.
- Precise Treatments: Technology facilitates accurate diagnostics and treatments. CAD/CAM ensures precise dental restoration design and manufacturing, while digital X-rays provide accurate imaging with reduced radiation.
- Patient Data Security: Digital dentistry’s rise necessitates robust data security. Encryption protocols protect patient records, and secure cloud storage allows safe data backup and access.
Technology in dental practices boosts care quality and patient experience, forecasting a promising, patient-centric dentistry future.
Ethical Considerations of Dental Technology
Dental technology advancements elevate patient care but also bring ethical challenges, notably in teledentistry. This field employs telecommunication for remote dental care, education, and consultation, raising ethical queries.
Practitioners must ensure remote care quality equals traditional face-to-face care, maintaining high diagnosis, treatment planning, and patient safety standards. Informed consent in virtual settings is critical, as the lack of a dentist’s physical presence may cause patients to overlook essential details.
Patient privacy is a significant ethical concern in dental technology due to digitization of records and digital imaging use, increasing data breach risks. Dentists must establish strong data security protocols to protect sensitive patient information, remaining transparent about data storage, usage, and sharing.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Potential Risks or Drawbacks of Integrating Technology in Dental Practices?
Integrating technology in dental practices presents risks such as Technological Reliability issues and Cybersecurity Challenges. Unsteady technology can disrupt operations. Cyber threats risk patient data, leading to privacy breaches and potential legal consequences.
How Does the Cost of Incorporating Advanced Technology Into Dental Practices Affect the Pricing of Dental Procedures?
Incorporating advanced technology into dental practices increases procedure costs due to high initial investment and maintenance. However, this technology acceptance may boost patient satisfaction, justifying the higher pricing.
How Can Patients Ensure Their Personal Information Is Secure When Using Digital Dentistry Services?
Patients secure personal data in digital dentistry by verifying robust data encryption use. Guidance from patient education programs can further enhance data protection.
What Kind of Training or Certifications Do Dentists Need to Use These Advanced Technologies?
Dentists need Technological Competence and Technology Acceptance training to use advanced dental technologies. Specific certifications, continuing education courses, and hands-on experience with the technology are often required.
Can Patients Opt Out of Using Digital Services and Request Traditional Methods Instead? if So, How Might This Affect Their Treatment?
Certainly, patients may choose traditional methods over digital services. However, this choice could influence the efficacy of their treatment due to extended traditional procedure times, possibly affecting patient comfort.
Conclusion
Technology integration in dentistry is transformative, enhancing diagnostics, refining treatments, and optimizing patient experiences. Ethical considerations govern its responsible adoption. Future dental innovations show immense potential, emphasizing the need for constant learning and adaptation in this swiftly changing field.